

Validation of MRI Classification System for Tibial Stress Injuries. Kijowski R, Choi J, Shinki K, Del Rio A, De Smet A. Diagnostic Imaging in Athletes with Chronic Lower Leg Pain.
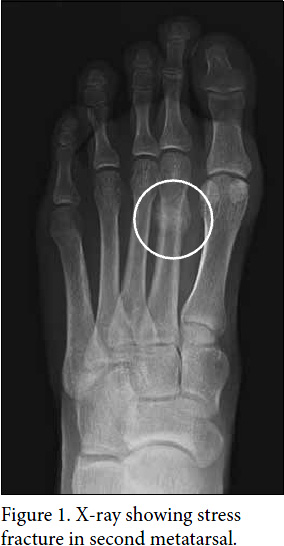
Shin Splints: MR Appearance in a Preliminary Study. High-Resolution CT Grading of Tibial Stress Reactions in Distance Runners. CT and MR Imaging Findings in Athletes with Early Tibial Stress Injuries: Comparison with Bone Scintigraphy Findings and Emphasis on Cortical Abnormalities. A Prospective Controlled Study of Diagnostic Imaging for Acute Shin Splints. Asymptomatic Tibial Stress Reactions: MRI Detection and Clinical Follow-Up in Distance Runners. Bergman A, Fredericson M, Ho C, Matheson G. chronic exertional compartment syndrome.tibial stress fracture: there can be some overlap depending on the definition.stress fractures are managed by removing the causative activity.medial tibial stress syndrome patients can continue running at reduced levels.stress fracture which will show early phase uptake). On the 3-phase isotope bone scan there will be typically normal appearances on the arterial and blood pool phases but longitudinal uptake on the delayed images. Nuclear medicineīone scintigraphy is relatively sensitive (~75%) 3 and may demonstrate high uptake in the affected region, characteristically along the posteromedial tibial aspect on lateral views. The Fredericson grading system can be used to grade the MRI findings with a good correlation with clinical severity and outcome 7,8. striation: may be seen as subtle intracortical linear hyperintensity.defined as loss of cortical signal void (MRI) resorption cavity is a round or oval intracortical area of increased signal intensity (MRI).bone remodeling: caused by osteoclast-mediated resorption and osteoblastic replacement and leads to changes in cortex.bone marrow edema: usually accompanied by periosteal edema at similar level as periosteal edema but usually on a shorter segment 14.periosteal edema: may be very subtle and noticeable in early stages, only on fluid-sensitive sequences (STIR, fat-suppressed T2- and PD).The axial fluid-sensitive, fat-saturated sequences are often the most helpful. The medial cortex (+/- posterior cortex) is most commonly affected 3. MRI is the most sensitive radiological examination (~88%) for medial tibial stress syndrome 3. It may demonstrate a spectrum of findings ranging from normal to periosteal fluid and marrow edema in medial tibial stress syndrome to a complete stress fracture 5. Medial tibial stress syndrome may show focal hyperechoic elevation of the periosteum with irregularity over the distal tibia and increased flow on Doppler interrogation. CTĬT is not particularly sensitive for medial tibial stress syndrome (~40%) 3. It may reveal mild osteopenia as an early sign of fatigue damage of cortical bone in tibial diaphysis 3,4. It may, however, demonstrate subtle periosteal reaction or callus around the cortex of the tibia medially 11. Radiographic features Plain radiographįor medial tibial stress syndrome, plain radiographs are considered insensitive and are often normal. Medial tibial stress syndrome is characterized by localized pain that occurs during exercise at the medial surface of the distal two-thirds of the tibial shaft.Ī "one-leg hop test" is a functional test, that can be used to distinguish between medial tibial stress syndrome and a stress fracture: a patient with medial tibial stress syndrome can hop at least 10 times on the affected leg whereas a patient with a stress fracture cannot hop without severe pain 2. Medial tibial stress syndrome typically occurs in runners and other athletes that are exposed to intensive weight-bearing activities such as jumpers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
